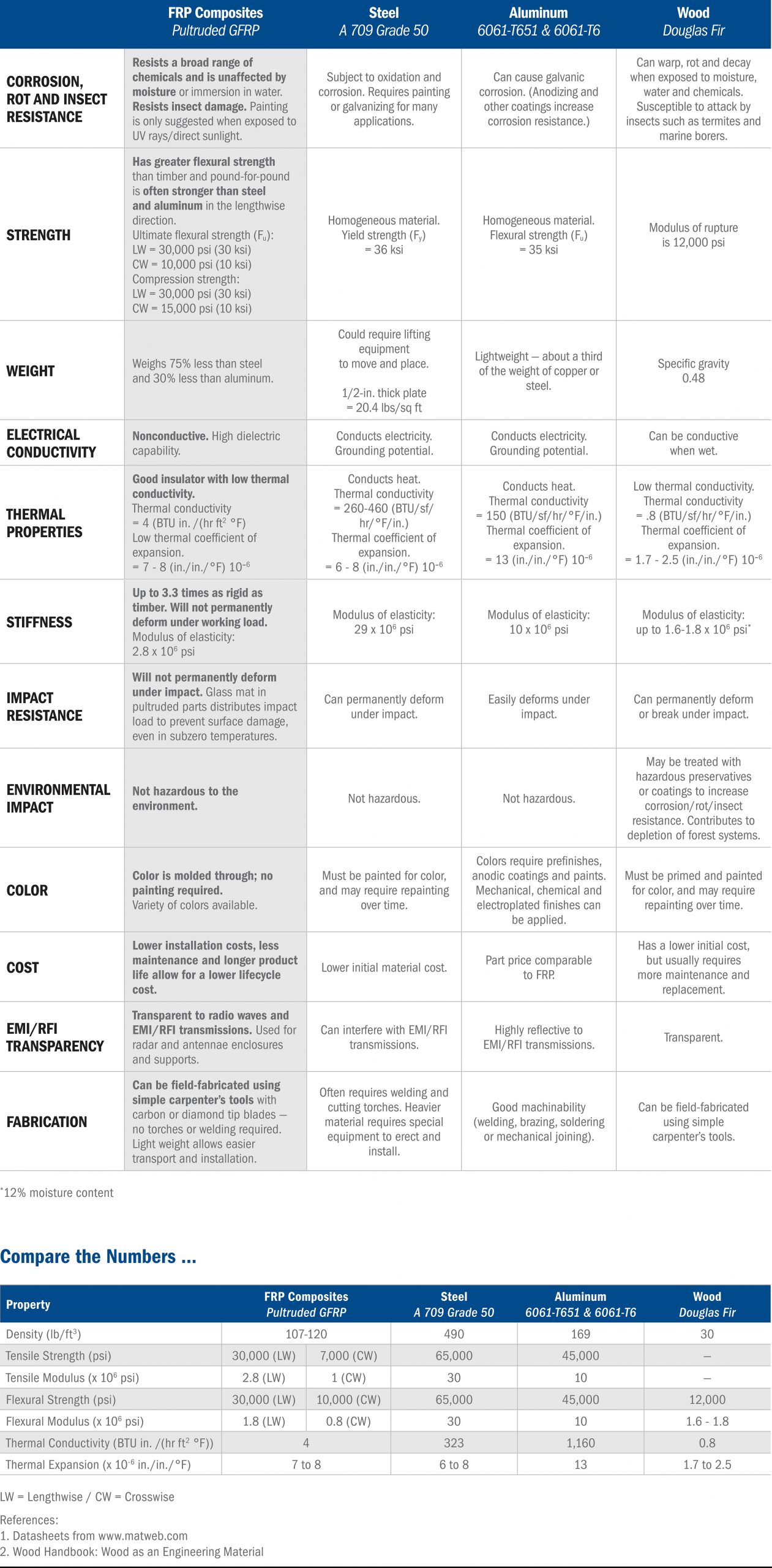
At LEADFRP, we believe that fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) products are the choice of the future. Compared with traditional materials such as steel and aluminum, it has excellent performance and service life.
LEADFRP provides a series of high-strength fiber reinforced plastic products (FRP), which are designed and manufactured to provide long-lasting performance in highly corrosive environments, while having the advantages of light weight and high dielectric strength compared with traditional structural materials.
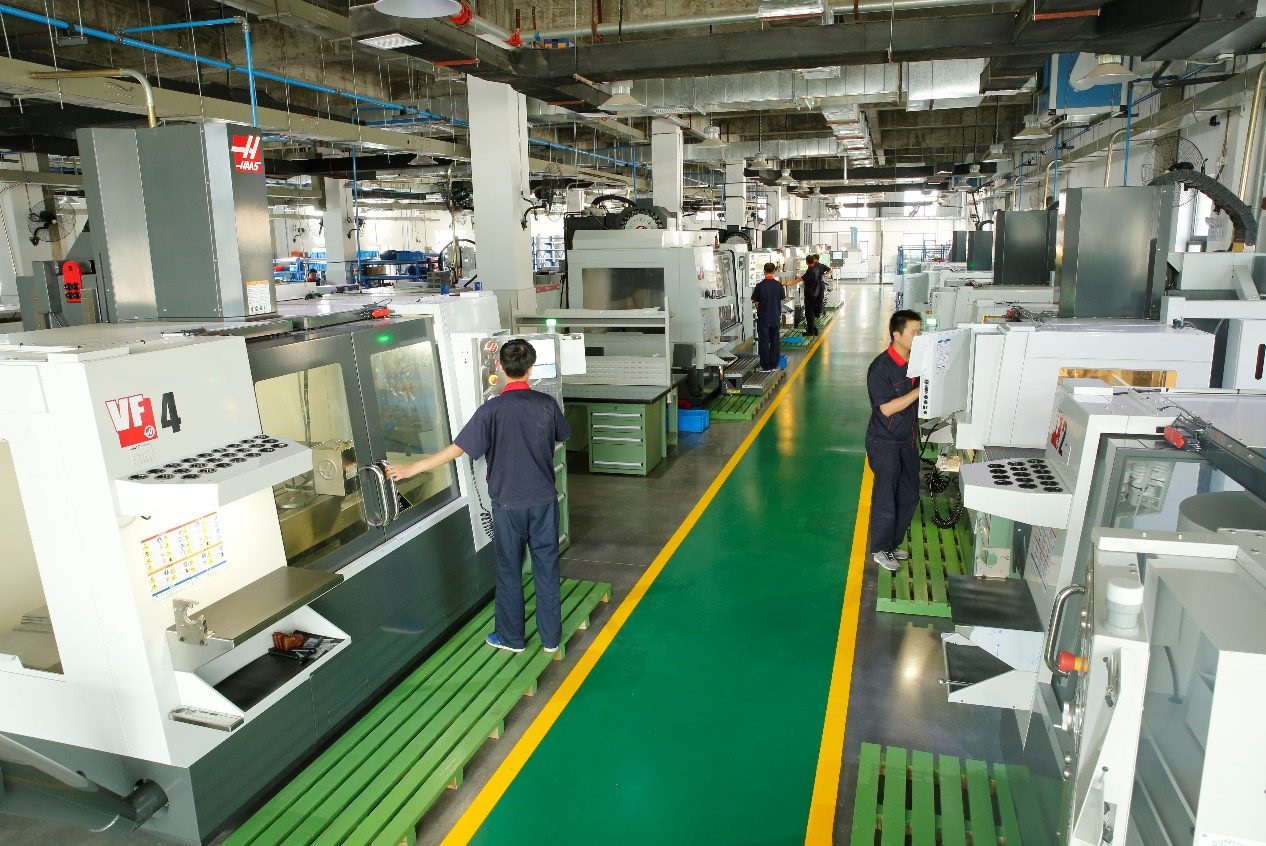
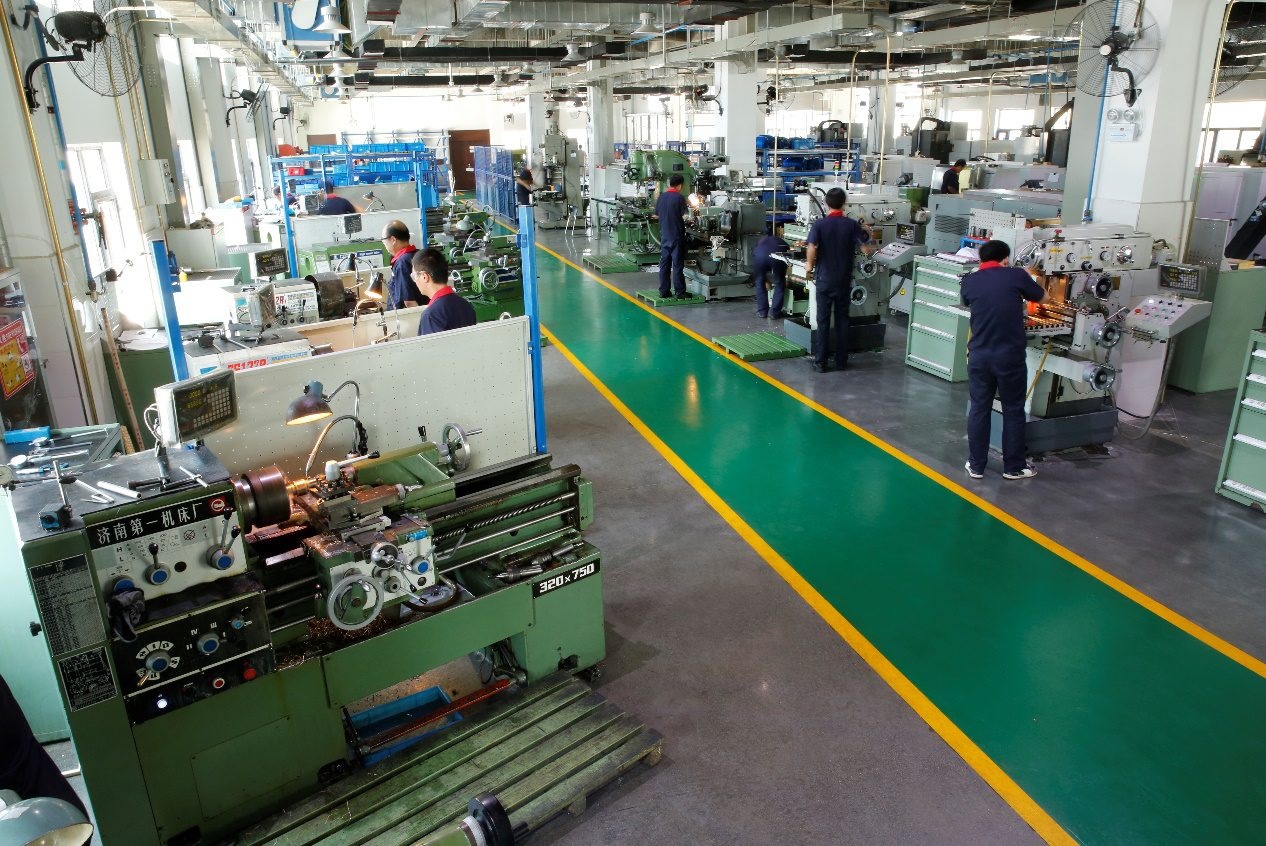
Since 2001, we have provided our customers with innovative, high-quality composite designs and materials through two strategic offices/factories located in the United States and China. It is here that we provide turnkey solutions to take your product from concept to design, to mold calculation, manufacturing, and finally to installation. [More about manufacturing]
We own 5 acres (20000 square metre) standard plants, 80 sets of advanced various manufacturing and machining equipments, 120 sets of assembly pultrusion production line, including one 1000 kN tensile strength machine and one 200 kN bending and torsion machine. We also can proceed basic property test of different kinds of composite insulation materials according to GB, ASTM, etc standards. Our products passed TUV Rheinland type test and UL type test.
LEADFRP strictly carry out standardized, scientific and normalized management mode. We fully implement ISO9001 quality management system, ERP managing system and 6S management mode through the whole service cycle of contract signing, production, process inspection, finished product ex-factory, after-sales service, which outstandingly reflect ‘Quality is the Life of Enterprise’. We have ISO9001, ISO14001 and ISO45001 identification.
Production Process:
Pultrusion, all Moulding type, Laminating, Casting Forming.
Feature Classification:
Food Grade, Flame Retardant, Conductive Type, anti-Corrosion, High Strength, Specific Surface.
Resin Types:
Epoxy, Polyester, Phenolic, Polyurethane, Acrylic, Polystyrene, Polypropylene, Polyethylene.
Fiber Type:
Carbon, E-Glass, ECR Glass, AR-Glass,Tow, Veil mats, Woven fabrics, Chopped strand mat.
Surface Avaliabe:
Glassfiber, Polyester, Special Type
Colors Avaliabe:
We recommend referring to RAL color standard
Size Avaliabe:
Customize Supported